Understanding Scaling
Scaling is the process of adding or removing resources to match the changing demands of your application. As your application grows, you will need to add more resources to handle the increased load. And as the load decreases, you can remove the extra resources to save costs.
Terraform makes it easy to scale your infrastructure by providing a declarative way to define your resources. You can define the number of resources you need and Terraform will automatically create or destroy the resources as needed.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, we have to set up AWS Provider, Region, VPC, InternetGateway, Security Group, and RouteTable.
COPY
COPY
📁 terraform/terraform-aws
--📄 terraform.tf
--📄 provider.tf
--📄 vpc.tf
--📄 subnet.tf
--📄 internetgateway.tf
--📄 routetable.tf
--📄 securitygroup.tf
Create a
terraform.tffile to declare AWS providers required for the system.terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 4.0" } } }
Create a
provider.tffile to specify the AWS region required for instance.provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" }
Create a
vpc.tffile to set up VPC for the ec2 instance.resource "aws_vpc" "main" { cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16" tags = { Name = "main" } }
Inside
subnet.tffile create 2 subnets (public, private) for auto-scaling group.```apache #public subnet resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
tags = { Name = "PublicSubnet" } }
private subnet
resource "aws_subnet" "private_subnet" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id cidr_block = "10.0.2.0/24"
tags = { Name = "PrivateSubnet" } }

5. Create an [`internetgateway.tf`](https://mizanf123.hashnode.dev/) file to configure the internet gateway.
```apache
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "my_igw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
tags = {
Name = "internet-getway"
}
}

Create a
routetable.tffile for routing public subnet to VPC.resource "aws_route_table" "public" { vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id route { cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.my_igw.id } tags = { Name = "PublicRouteTable" } } resource "aws_route_table_association" "public_subnet" { subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet.id route_table_id = aws_route_table.public.id }
Create a
securitygroup.tffile which will create a security group that allows SSH, HTTP, HTTPS, and egress traffic to the instances.resource "aws_security_group" "web_server" { name_prefix = "web-server-sg" vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id ingress { from_port = 80 to_port = 80 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } ingress { from_port = 22 to_port = 22 protocol = "tcp" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } egress { from_port = 0 to_port = 0 protocol = -1 cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } }
Task 1: Create an Auto Scaling Group
Now create a
main.tffile. In yourmain.tffile, add the following code to create an Auto Scaling Group:resource "aws_launch_configuration" "web_server_as" { image_id = "ami-053b0d53c279acc90" instance_type = "t2.micro" security_groups = [aws_security_group.web_server.id] user_data = <<-EOF #!/bin/bash sudo apt-get update -y sudo apt-get install apache2 -y sudo systemctl start apache2 sudo systemctl enable apache2 sudo systemctl restart apache2 sudo chmod 766 /var/www/html/index.html sudo echo "<html><body><h1>Welcome to Terraform Scaling.</h1></body></html>" >/var/www/html/index.html EOF } resource "aws_elb" "web_server_lb"{ name = "web-server-lb" security_groups = [aws_security_group.web_server.id] subnets = [aws_subnet.public_subnet.id,aws_subnet.private_subnet.id] listener { instance_port = 8000 instance_protocol = "http" lb_port = 80 lb_protocol = "http" } tags = { Name = "terraform-elb" } } resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "web_server_asg" { name = "web-server-asg" launch_configuration = aws_launch_configuration.web_server_as.name min_size = 1 max_size = 3 desired_capacity = 2 health_check_type = "EC2" load_balancers = [aws_elb.web_server_lb.name] vpc_zone_identifier = [aws_subnet.public_subnet.id] tag { key = "Name" value = "web-server-as" propagate_at_launch = true } }
Apply Your Terraform Configuration
Run
terraform applyin the terminal to apply your Terraform configuration.
Type yes

Verify
Once Terraform completes execution, verify that the Auto Scaling Group is created with the desired settings in the AWS Auto Scaling Group dashboard.


Task 2: Test Scaling
Go to the AWS Management Console and select the Auto Scaling Groups service.

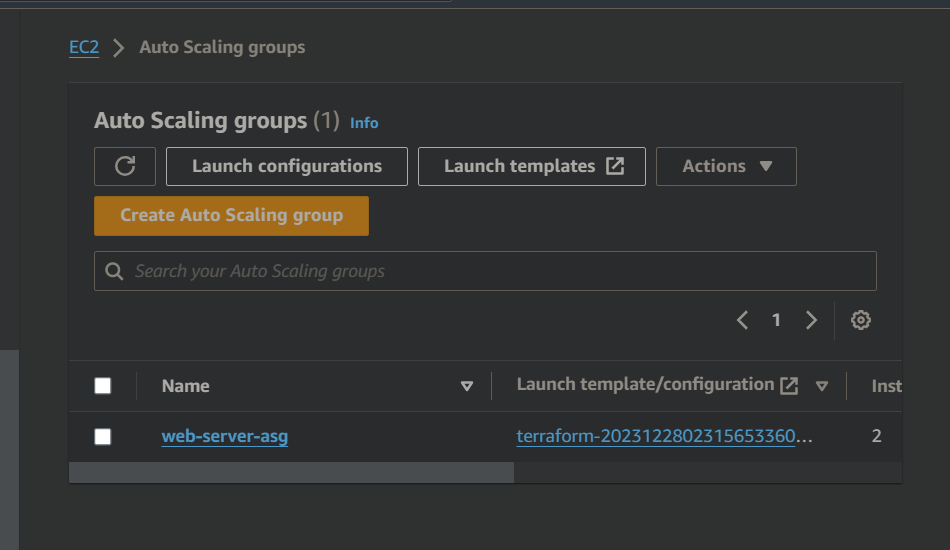
Select the Auto Scaling Group you just created and click on the "Edit" button.

Increase the "Desired Capacity" to 3 and click on the "Save" button.

Wait a few minutes for the new instances to be launched. Go to the EC2 Instances service and verify that the new instances have been launched.

Decrease the "Desired Capacity" to 1 and wait a few minutes for the extra instances to be terminated.

Go to the EC2 Instances service and verify that the extra instances have been terminated.

Connect with me:)
Thank you for diving into this blog with me! I trust you found the information both helpful and enlightening. To stay updated on the latest in DevOps 🚀, make sure to follow me. Remember, staying informed means staying ahead in the dynamic world of DevOps!
Feel free to connect with me on:
For more updates and engaging discussions on DevOps, let's connect! 🚀 #DevOpsCommunity
