Table of contents
- Introduction to Ansible Playbook
- Prerequisites:
- Tasks:)
- Task-01: Write an ansible playbook to create a file on a different server
- Task-02: Write an ansible playbook to create a new user.
- Task-03: Write an ansible playbook to install docker on a group of servers
- Task-04: Create a playbook to install Nginx
- Task-05: Deploy a sample webpage using the ansible playbook
- Connect with me:)
Introduction to Ansible Playbook

An Ansible playbook is a structured document that defines a set of tasks, configurations, and plays to be executed by Ansible
Ansible playbooks run multiple tasks, assign roles, and define configurations, deployment steps, and variables. If you’re using multiple servers, Ansible playbooks organize the steps between the assembled machines or servers and get them organized and running in the way the users need them to. Consider playbooks as the equivalent of instruction manuals.
It is written in YAML (YAML Ain't Markup Language) and serves as the central component for defining automation workflows in Ansible.
Key components of an Ansible playbook include:
Hosts: Specifies the target hosts or groups on which the playbook tasks will be executed.
Tasks: Describes a list of actions or operations to be performed on the target hosts. Each task typically corresponds to an Ansible module that carries out a specific action, such as installing a package, copying files, or restarting services.
Plays: A play is a set of tasks that are executed on a specific group of hosts. Plays allow you to organize and structure your automation tasks logically.
Handlers: Handlers are tasks that respond to specific events triggered by other tasks in the playbook. For example, restarting a service after a configuration file change.
Variables: Ansible playbooks can use variables to make them more flexible and reusable. Variables can be defined within the playbook or in external files.
Basic Syntax:
---
- name: Playbook Name
hosts: target_hosts
become: yes # Optional, to execute tasks with elevated privileges
vars:
variable_name: variable_value # Optional, define variables for the playbook
tasks:
- name: Task 1 Description
module_name:
parameter1: value1
parameter2: value2
- name: Task 2 Description
module_name:
parameter1: value1
parameter2: value2
handlers:
- name: Handler 1
module_name:
parameter1: value1
parameter2: value2
- name: Handler 2
module_name:
parameter1: value1
parameter2: value2
Explanation:
name: Descriptive name for the playbook, tasks, and handlers.hosts: Specifies the target hosts or groups on which the playbook tasks will be executed.become: (Optional) Indicates whether tasks should be executed with elevated privileges (sudo).vars: (Optional) Define variables for the playbook to enhance flexibility.tasks: List of tasks to be executed on the target hosts. Each task involves a specific Ansible module and its parameters.handlers: (Optional) List of handlers, which are tasks triggered by specific events. Handlers are defined separately but are called by tasks when needed.
Prerequisites:
Ansible Installed on the Master Node:
Server Nodes:

Connection Established Between Master and Server Nodes:
This is blog for refresence
Optional: Playbook Folder on the Master Node:

Tasks:)
Task-01: Write an ansible playbook to create a file on a different server
Step 1: Create the playbook file (create_file.yml):
Step 2: Write the Content:
---
- name: Create a file on a different server
hosts: your_target_server # Replace with the hostname or IP of your target server
become: true # To run tasks with elevated privileges
tasks:
- name: Create a file
file:
path: /path/to/remote/file.txt # Replace with the desired remote path and filename
state: touch
Open your preferred text editor (e.g., VSCode, Nano, Vim) and paste the content of the playbook into a new file named
create_file.yml.Replace
your_target_serverwith the actual hostname or IP address of the server where you want to create the file.Modify
/path/to/remote/file.txtto the desired path and filename on the remote server.

Step 3: Apply the Playbook:
Run the following command in the same directory as your playbook file:
ansible-playbook create_file.ymlAnsible will execute the playbook, and the file will be created on the specified server.

Step 4: Verify: (This verify is done on the server 1)
SSH into the target server to verify that the file has been created.
ssh <username>@<your_target_server> ls /path/to/remote/Replace
<username>with your SSH username and<your_target_server>with the hostname or IP address of the target server.
Task-02: Write an ansible playbook to create a new user.
Step 1: Create the playbook file (create_user.yml)

Step 2: Write the Content:
Open your preferred text editor (e.g., VSCode, Nano, Vim) and paste the content of the playbook into a new file named
create_user.yml.Replace
your_target_serverwith the actual hostname or IP address of the server where you want to create the new user.Modify
your_new_userto the desired username you want to create.
---
- name: Create a new user on a server
hosts: your_target_server # Replace with the hostname or IP of your target server
become: true # To run tasks with elevated privileges
tasks:
- name: Create a new user
user:
name: your_new_user # Replace with the desired username
state: present

Step 3: Apply the Playbook:
Run the following command in the same directory as your playbook file:
ansible-playbook create_user.ymlAnsible will execute the playbook, and the new user will be created on the specified server.

Step 4: Verify:
Just for check - connect the server 1 using ssh then
cat /etc/passwd | grep <your_new_user>
Task-03: Write an ansible playbook to install docker on a group of servers
Step 1: Create the Playbook File Create a new file named install_docker.yml to store your playbook.
Step 2: Write the Playbook Content Add the following content to your install_docker.yml file:
---
- name: Install Docker
hosts: your_server_group
become: true
tasks:
- name: Add Docker GPG key
apt_key:
url: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg
state: present
- name: Add Docker APT repository
apt_repository:
repo: deb https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu focal stable
state: present
- name: Install Docker
apt:
name: docker-ce
state: present
Replace your_server_group with the name of the group where you want to install Docker.

Step 3: Apply the Playbook Run the following command to apply the playbook:
ansible-playbook install_docker.yml

Step 4: Verify After applying the playbook, SSH into one of the servers in your group and run the following command to verify that Docker has been installed:
docker --version
You should see information about the Docker version if the installation was successful.
I check with the following command
sudo docker ps

Task-04: Create a playbook to install Nginx
Certainly! Here's a step-by-step guide to creating an Ansible playbook to install Nginx:
Step 1: Create the Playbook File Create a new file named install_nginx.yml to store your playbook.
Step 2: Write the Playbook Content Add the following content to your install_nginx.yml file:
---
- name: Install Nginx
hosts: your_server_group
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update apt cache
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: latest
- name: Start Nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: started
Replace your_server_group with the name of the group where you want to install Nginx.

Step 3: Apply the Playbook Run the following command to apply the playbook:
ansible-playbook install_nginx.yml

Step 4: Verify After applying the playbook, open a web browser and enter the IP address or hostname of one of the servers in your group. You should see the default Nginx welcome page.


That's it! You've created an Ansible playbook to install and start Nginx on a group of servers.
Task-05: Deploy a sample webpage using the ansible playbook
Certainly! Let's enhance the previous playbook to deploy a sample webpage along with installing Nginx. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Modify the Playbook File Open your install_nginx.yml playbook and modify it to include the deployment of a sample webpage. Add the following tasks:
---
- name: Install Nginx and Deploy Sample Webpage
hosts: your_server_group
become: true
tasks:
- name: Update apt cache
apt:
update_cache: yes
- name: Install Nginx
apt:
name: nginx
state: latest
- name: Start Nginx
service:
name: nginx
state: started
- name: Deploy Sample Webpage
copy:
src: sample/index.html
dest: /var/www/html/index.html
In this example, assume you have a sample folder with an index.html file containing your sample webpage.

Step 2: Create the Sample Webpage Create a folder named sample and add an index.html file with your desired webpage content.

Step 3: Apply the Updated Playbook Run the following command to apply the updated playbook:
ansible-playbook install_nginx.yml
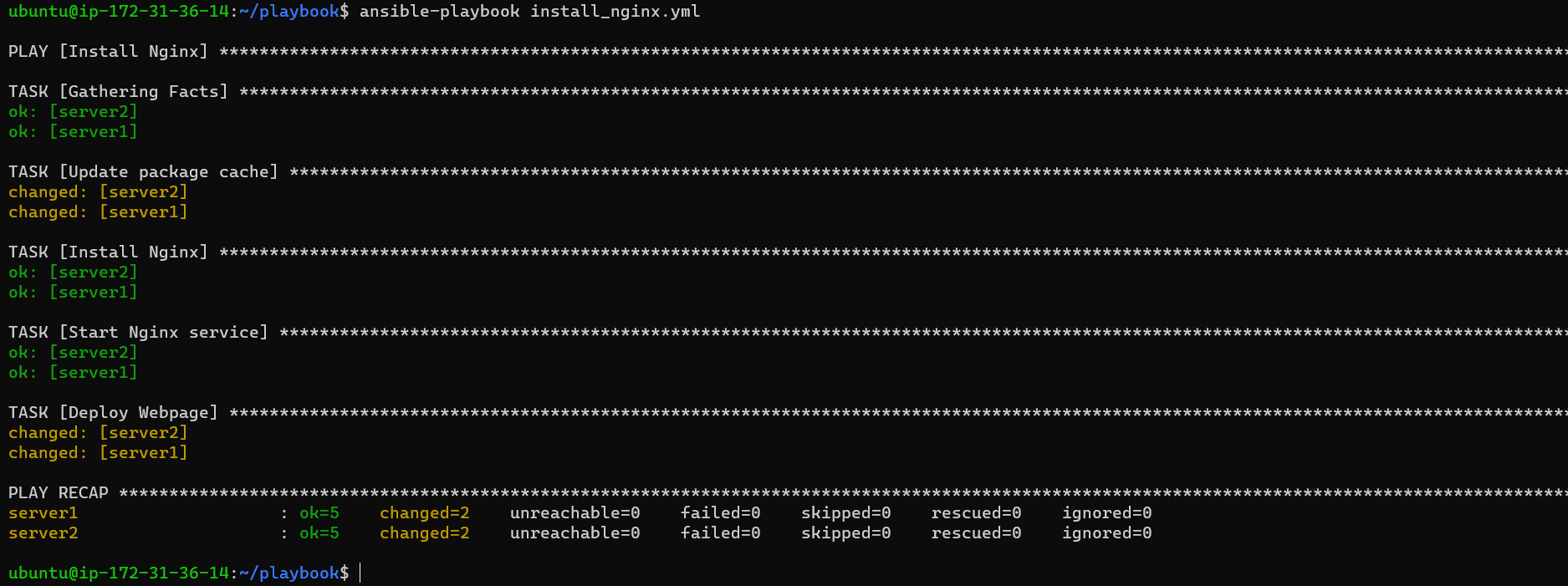
Step 4: Verify Open a web browser and enter the IP address or hostname of one of the servers in your group. You should now see your deployed sample webpage.

Congratulations! You've expanded your Ansible playbook to install Nginx and deploy a sample webpage.
Connect with me:)
Thank you for diving into this blog with me! I trust you found the information both helpful and enlightening. To stay updated on the latest in DevOps 🚀, make sure to follow me. Remember, staying informed means staying ahead in the dynamic world of DevOps!
Feel free to connect with me on:
For more updates and engaging discussions on DevOps, let's connect! 🚀 #DevOpsCommunity

